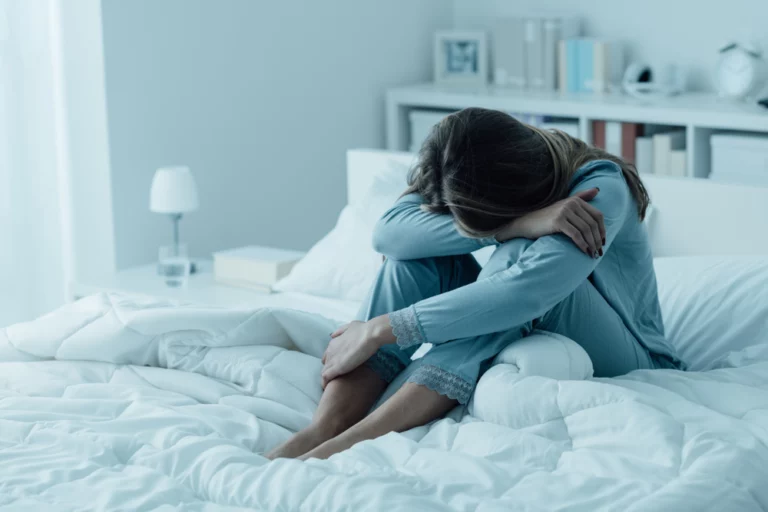
If you’ve noticed a change in your loved one’s behavior recently, you might be worried that they’ve developed a mental health disorder like bipolar disorder and addiction. Anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder can affect one’s behavior, making them seem off or different. Addiction can also bring about similar behaviors and symptoms. If you notice a change in a loved one, you might want to pry and try and figure out what’s going on.
This might not be the best way to go about things. By being a friend and supporting them through the hard time they’re experiencing, they may open up to you. Open and honest communication is important in these difficult situations and can help both you and your loved one immensely.
However, how can you tell the difference between bipolar disorder and addiction? How can you tell if your loved one is sad or if they have a mental disorder? Use this guide to learn about the signs of bipolar disorder and how you can help your loved one seek treatment.
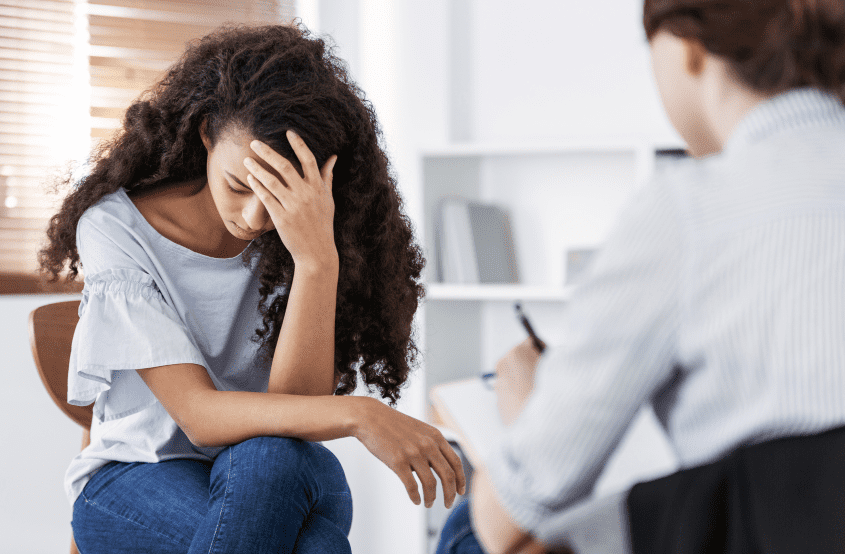

What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a mood disorder that can cause intense mood swings. These mood swings may occur rapidly or over a long period of time. Those with bipolar disorder often switch from feeling manic to feeling depressed or the other way around. They may also experience both moods at the same time.
There are a few types of bipolar disorder:
- Bipolar I disorder involves manic episodes that last seven days or longer. These episodes often require medical attention. Depressive episodes may still occur.
- Bipolar II disorder involves depressive episodes and shorter manic episodes that don’t last as long. This is referred to as hypomania. This type of mania is usually less severe.
- Cyclothymic disorder involves both types of episodes, but the episodes are as intense or as long as in other disorder types. Cyclothymic disorder isn’t lifelong and usually only lasts for one to two years.
What Can Bipolar Disorder and Addiction Look Like?
Addiction is a complex and multifaceted condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age, background, or socioeconomic status. It is characterized by the inability to control the use of a substance or engagement in a behavior, despite negative consequences. Recognizing the symptoms and signs of addiction is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. While the specific manifestations may vary depending on the substance or behavior involved, there are common physical, emotional, and behavioral indicators to watch for.
Physical Symptoms
One of the most apparent signs of addiction is the presence of physical changes. These may include sudden weight loss or gain, bloodshot eyes, poor hygiene, or unexplained bruises or marks on the body. For substance addictions, individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms such as nausea, sweating, tremors, or headaches when the substance is not available. Changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia or excessive sleeping, are also common. Over time, addiction can lead to chronic health issues, including liver damage, heart problems, or respiratory issues, depending on the substance abused.
Emotional and Psychological Signs
Addiction often takes a toll on mental health. Individuals may exhibit mood swings, irritability, or unexplained outbursts of anger. They may become increasingly anxious, depressed, or paranoid, especially when unable to access the substance or engage in the addictive behavior. A noticeable lack of motivation, apathy, or a decline in interest in activities they once enjoyed can also signal a problem. In some cases, individuals may experience memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, or impaired judgment.
Behavioral Changes
Behavioral changes are often the most telling signs of addiction. These may include secrecy, lying, or avoiding friends and family to hide the extent of the problem. Individuals may neglect responsibilities at work, school, or home, leading to a decline in performance or attendance.
Financial issues may arise due to spending excessive amounts of money on the substance or behavior. Social withdrawal and a shift in social circles, particularly toward others who share the addiction, are also common. In severe cases, individuals may engage in risky behaviors, such as driving under the influence or stealing, to sustain their addiction.
Recognizing these symptoms and signs is the first step toward seeking help. Addiction is a treatable condition, and with the right support, individuals can regain control of their lives and move toward recovery. If you or someone you know is exhibiting these signs, reaching out to a healthcare professional or support group can make all the difference.
Signs and Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder and Addiction
If you believe something is going on with your loved one, you should watch out for the following signs. Because bipolar disorder can cause both depression and mania, you should be on the lookout for symptoms and signs that match either of the following categories.
Signs of Depression
If your loved one has seemed more sad or upset lately, this could be a sign of a depressive cycle. However, it can be difficult to tell the difference between sadness and depression. Depression often lasts for a longer amount of time and can have other side effects including:
- Frequently missing work or school
- Having little energy
- Sleeping too much or too little
- Lack of interest
- Thinking about or attempting suicide
- Feeling hopeless or worthless
- Eating too much or too little
- Talking slowly
- Forgetfulness
- Isolating or feeling lonely
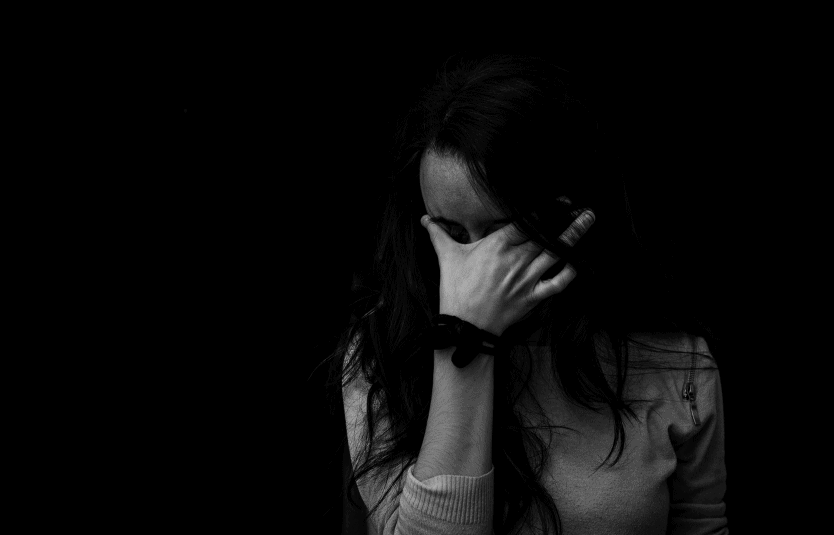

Signs of Mania
On the other hand, signs of mania are quite the opposite. If you notice signs of a manic episode (especially following a depressive episode), you may want to help your loved one seek treatment for potential bipolar disorder. Signs of mania include:
- Feeling high, “up”, or elated
- Feeling jumpy or more active
- Racing thoughts
- Speaking quickly
- Sleeping less than usual
- Feeling unusually confident or powerful
- Having a short temper
- Irratbility
- Poor judgment
- Impulsivity
The Overlapping Signs of Bipolar Disorder and Addiction
Bipolar disorder and addiction are both complex conditions that can deeply impact a person’s life, and though they are distinct diagnoses, they share several overlapping symptoms and behaviors. Understanding these similarities can help in better identifying and treating individuals who may be struggling with one or both issues.
One of the most prominent shared traits between bipolar disorder and addiction is impulsivity. During manic or hypomanic episodes of bipolar disorder, individuals may engage in reckless behavior such as overspending, unsafe driving, or risky sexual behavior. Similarly, those struggling with addiction may exhibit impulsive actions, such as using substances in dangerous situations or pursuing high-risk activities to satisfy cravings. In both cases, these impulsive actions can stem from an impaired ability to evaluate consequences, leading to negative outcomes for the person involved.
Another shared symptom is mood instability. In bipolar disorder, mood swings between manic (elevated or irritable) and depressive episodes are common, while in addiction, people may experience drastic mood shifts as they move between the euphoria of substance use and the lows associated with withdrawal. These mood swings can lead to erratic behavior, strained relationships, and a general lack of stability in daily functioning, making it difficult to predict a person’s emotional state or actions from day to day.
Both conditions can also drive an intense need for escape. In the case of bipolar disorder, individuals may seek relief from depressive episodes or the overwhelming nature of mania by engaging in activities that offer temporary emotional highs. Substance abuse often serves a similar purpose for people with addiction: using drugs or alcohol to escape from stress, anxiety, or emotional pain. This desire for an emotional escape creates a cycle where substance use and mood disorders feed into each other, making it harder for individuals to break free from either condition.
Furthermore, both bipolar disorder and addiction can lead to destructive consequences in a person’s personal, professional, and social life. Relationships may suffer, and individuals may experience job loss, financial instability, and legal trouble. The stigma surrounding both conditions can also prevent individuals from seeking help or being understood by those around them.
While bipolar disorder and addiction share common symptoms, it’s important to note that they are distinct conditions that require specific treatments. Dual diagnosis, when someone is affected by both, is a common scenario, and addressing both issues simultaneously is crucial for successful recovery. Early diagnosis, compassionate care, and tailored treatment plans are essential to improving outcomes for individuals managing these co-occurring conditions.
Struggling with Bipolar Disorder and Addiction? Knoxville Recovery Center Can Help
If you believe that your loved one is struggling with bipolar disorder, it’s important to speak with us about your options. Mental health treatment can include therapy and medication and is incredibly beneficial for bipolar patients. If you or your loved one is looking for holistic treatment in Knoxville, TN, we’re here to help.
For more information or to learn more about our treatment options, contact us or call Knoxville Recovery Center today.